PROMYDE BIO FAQS
ANSWERS TO THE MOST FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT PROMYDE BIO
What are the main properties of Promyde BIO?

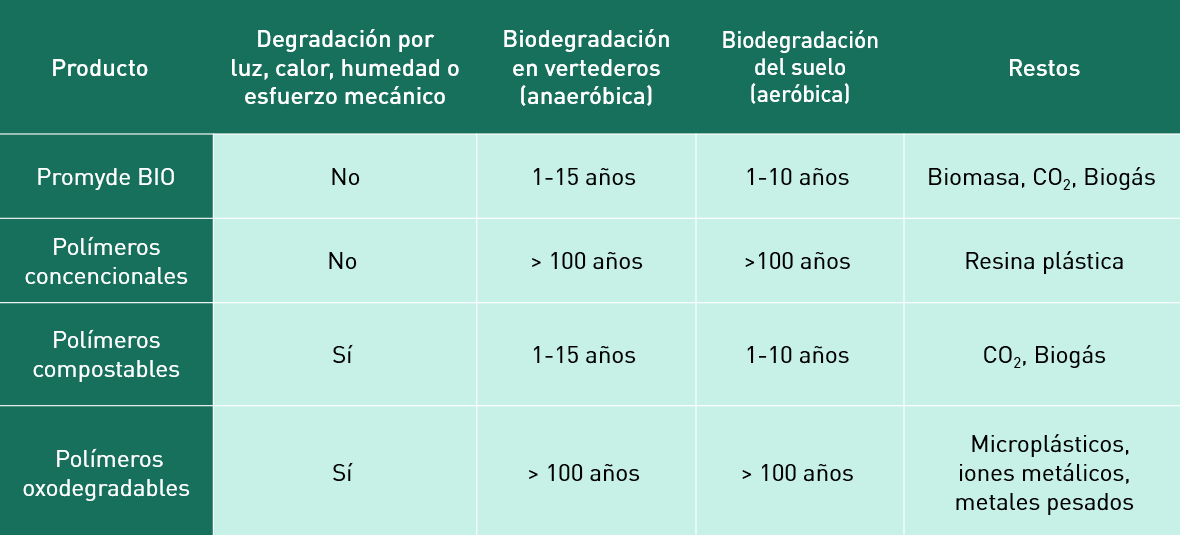
Promyde BIO maintains the same physical properties and strength of standard Promyde grades. Products made from this material will have an indefinite shelf life, unaffected by light, heat, moisture or mechanical stress, until they are disposed of in an active microbial environment, such as a landfill or soil. Under these conditions, Promyde BIO will biodegrade into biomass,CO2 and biogas.
What is the difference between biodegradable, compostable and degradable plastics?

Biodegradable plastic: It degrades through the action of microorganisms in aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (without oxygen) environments in an unspecified period of time.
Compostable Plastic: Decomposes under composting conditions intoCO2, water, inorganic compounds and biomass, complying with standards such as EN13432, within a specified period.
Degradable plastic: Undergoes significant chemical changes under environmental conditions, resulting in a loss of physical properties. These changes are usually initiated by factors such as oxygen, UV light or heat. This type of plastic begins to degrade as soon as it is manufactured, leading to a shorter service life. In Europe, oxo-degradable polymers are banned due to their negative environmental effects.
Do conventional plastics biodegrade?

Conventional plastics are durable and are not designed to biodegrade easily. These materials are valued for their physical properties, strength and durability. Most plastics are composed primarily of carbon atoms bonded together in long chains. Although carbon is an excellent source of nutrients for microorganisms, the structure of the long chains makes it difficult for them to be metabolized by microorganisms.
How does Promyde BIO biodegrade?

Promyde BIO is able to accelerate biodegradation thanks to its advanced technology, promoting the accumulation of microorganisms and facilitating the acclimatization and production of enzymes that allow their metabolization.
Promyde BIO maintains the physical properties and strength of standard Promyde grades, but is specifically formulated to biodegrade in microbially active environments, such as landfills and soils. In these environments, Promyde BIO breaks down into biomass, CO₂ and biogas, providing a more sustainable and environmentally friendly solution.
Does Promyde BIO degrade during storage?

No, Promyde BIO requires an active microbial environment, such as a landfill, in order to biodegrade. It will not degrade under normal storage conditions, such as in warehouses or on store shelves.
How long does it take for Promyde BIO to biodegrade?

Biodegradation time varies depending on factors such as surface area, mass, thickness and environmental conditions. Under optimized conditions, Promyde BIO can achieve up to 24.7% biodegradation in 160 days in anaerobic environments and up to 76% biodegradation in active soil in 90 days.
What tests validate the biodegradation of plastics in a landfill?

Laboratories use standardized tests to validate the biodegradability of plastics in a landfill. These tests include:
- ASTM D5511: To evaluate short-term biodegradability in landfill.
- ASTM D5526: For simulation of long-term landfill conditions.
Each test has its specific approach and limitations, so results should not be compared directly.
Can Promyde BIO be used in food contact applications?

Yes, if the standard version of Promyde complies with FDA and EU food contact regulations, then Promyde BIO will also be suitable for such applications.
What is the benefit of depositing Promyde BIO in a landfill?

Promyde BIO offers the benefit of reducing the long-term impact of plastic waste by biodegrading and producing methane. Methane can be recovered as a clean and economical energy source.
Is Promyde BIO biodegradable in soil?

Yes, Promyde BIO has demonstrated up to 76% biodegradation in soil within 90 days according to ISO 17556. Currently, we are conducting a new comprehensive test for up to 2 years to determine compliance with certifications such as OK biodegradable SOIL by TÜV AUSTRIA or Biodegradable in soil by DIN Certco (EN17033), achieving the following requirements:
- The maximum time for the biodegradation test (according to ISO 17556) will be a maximum of 2 years.
- The required percentage of relative biodegradation to be achieved is 90%, compared to cellulose.
- Other requirements in terms of ecotoxicity, nitrification, etc.
What is ISO 17556 about?

ISO 17556 describes the methodology for testing biodegradation in soil.
Standard procedure indicates that it is preferable to test the material in powder format, but it can also be used in film, fragment, chip or profile format.
Only 100-300 g of the material is used for the test. The maximum size of the material should be 5×5 mm. It is always recommended to compare different polymers using the same format. For example, standard PA versus Promyde BIO, as we did.
Is certification of the part or final product required?

Biodegradability is an intrinsic characteristic of materials, independent of the size, shape or thickness of the final product.
You can declare that your products are made with 100% Promyde BIO, which is a biodegradable polymer, and name the biodegradation rates declared by Promyde BIO in both aerobic and anaerobic environments following ISO17556 and ASTM 6511 standards.
In which applications is Promyde BIO recommended?

Promyde BIO has been designed for those applications with high technical requirements, where compostable polymers do not meet. It is recommended for applications with a short shelf life and for end products that are not effectively recycled or disposed of in a convenient manner.
Do you want to know all the news of Nurel Polymers?
Subscribe to the Newsletter